| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- union find
- MYSQL
- Trie
- Two Points
- Brute Force
- 그래프
- SQL
- String
- Dijkstra
- 이진탐색
- binary search
- Hash
- two pointer
- Stored Procedure
- 다익스트라
- 스토어드 프로시저
- DP
Archives
- Today
- Total
codingfarm
트라이 알고리즘 (trie) 본문
- 문자열 검색에서 매우 빠른 성능을 보이는 알고리즘
- 여러 기업에서 난이도 있는 문제의 주제로 자주 출제되는 추세이다.
가령
to, tea, ted, ten, a, inn
6개의 단어에 대해 trie 알고리즘을 적용했을 때 트리의 구조는 아래와 같다.
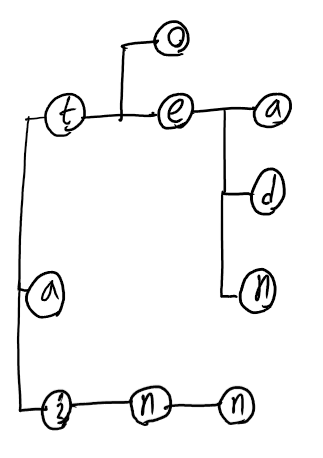
트라이 노드의 내부 구조는 단순하다.
자신과 같은 타입의 노드를 자식노드라 가지며
새로운 단어를 추가하거나 초기화 하기 위해선 해당 함수를 재귀적으로 호출하면 된다
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
|
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int GetChar(char ch) {
return ch - 'a';
}
class TrieNode {
public:
bool isEnd;
TrieNode* nodes[26];
int value;
TrieNode() {
isEnd = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
nodes[i] = 0;
}
void Clear() {
value = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (nodes[i] != 0) {
nodes[i]->Clear();
delete nodes[i];
}
nodes[i] = 0;
}
}
void Insert(string str, int value, int index = 0) {
int ch = GetChar(str[index]);
if (nodes[ch] == 0)
nodes[ch] = new TrieNode();
if (str.size() == index) {
isEnd = true;
this->value = value;
}
else nodes[ch]->Insert(str, value, index + 1);
}
int Find(string str, int index = 0) {
int ch = GetChar(str[index]);
if (str.size() == index) {
if (isEnd == true)
return value;
else
return -1;
}
if (nodes[ch] != 0) return nodes[ch]->Find(str, index + 1);
else return -1;
}
void Print(string& str) {
cout << str << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (nodes[i] != 0) {
str.push_back(i + 'a');
nodes[i]->Print(str);
str.pop_back();
}
}
}
};
int main(void) {
TrieNode dictionary;
dictionary.Clear();
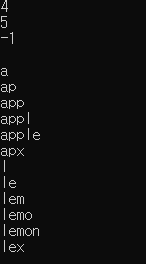
dictionary.Insert("apple", 4);
dictionary.Insert("lemon", 5);
cout << dictionary.Find("apple") << endl;
cout << dictionary.Find("lemon") << endl;
cout << dictionary.Find("melon") << endl;
string str;
dictionary.Print(str);
dictionary.Clear();
return 0;
}
|
cs |
'Algorithm & Data structure > 이론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 비트연산 (0) | 2021.04.19 |
|---|---|
| 완탐 (0) | 2021.04.19 |
| 구간 길이 구하기 (0) | 2021.01.06 |
| BST(Binary Search Tree) (0) | 2020.09.06 |
| Heap (0) | 2020.09.06 |
Comments
